A pump is a mechanical device used to move fluid from one point to another by transferring the energy generated by the main motor to the fluid. The main motor can be an electric motor, an I.C, a steam engine, or a turbine. The force mandatory to transfer the fluid varies according to the fluid volume, the height to be lifted (head), and the viscosity of the liquid.
A centrifugal pump is a most efficient pump compared to other types of pumps.
How does a Pump work?
There are different types of pumps, and each pump works differently. However, the basic principle is the same. Here we explain the general working principle of the pump.
We explain step by step!
Step 1
The pump connects to the motor or engine or any other driver; the driver must start.
Step 2
We already know that pumps move fluid from one place to another. Therefore, it is necessary to inject liquid into the pump. In the case of a reciprocating pump, negative pressure builds up in the cylinder due to the movement of the piston.
But centrifugal pumps need to be set up because the impeller cannot cause a large pressure difference in the pump.
Step 3
The pressure must not be less than the vapor pressure. Otherwise, the cavitation and bubbles will form and be damage the pump.
Step 4
Volutes and diffusers in the centrifugal pumps help to increase the fluid pressure. The rotation of the impeller causes centrifugal force, and this force also affects the liquid.
In the screw, water is transported (gradual increase in cross-section), the speed is reduced, and the pressure changes more.
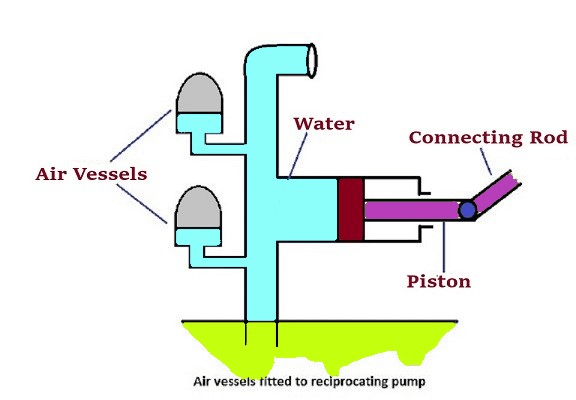
In the case of the reciprocating pump, the piston connects with the impeller via a connecting rod at the crankshaft and driver. After drawing in the liquid, the piston moves in the opposite direction and causes pressure in the liquid.
Types of Pumps
The pumps have the following types:
Centrifugal Pumps
The principle of operation of the centrifugal pump is the centrifugal force that is applied to each object as it rotates. The liquid entering the impeller hole comes into contact with the rotating impeller and absorbs its kinetic force. The centrifugal force pressurizes this liquid to move it towards the environment of the impeller.
As the liquid exits around the impeller, it enters the volute or diffuser chamber, where the force driving converts it into pressure. This pressure in the liquid causes it to advance through the tube to the delivery point. Multiple impellers can be mounted on the shaft, and they work in similarly constructed housing. These types of pumps are called two, three, or more stage centrifugal pumps.
Displacement Pumps
There are two main types of displacement pumps:
- Reciprocating pumps
- Rotary pumps
There are many variants of reciprocating piston pumps. Likewise, there are different types of rotary piston pumps, such as gear pumps, screw pumps, and vane pumps. All reciprocating pumps work on the principle that the moving parts of the pump physically replace fluids.
The piston of the reciprocating pump is moved up and down by the crankshaft rotated by the electric motor. The space above the piston is connected to the intake and transmission lines via intake and transmission valves. As the piston goes down, the intake valve opens, and liquid enters the intake tube and fills the cylinder space above the piston. Likewise, as the piston moves upward, the liquid in the space above the piston is pumped into the feed tube through the feed valve.
When only the space above the piston is used, the pump is called a single-acting pump. But a suction and discharge valve can also be installed under the piston, connected to the suction pipe and the discharge pipe, and can be used as a separate unit. The pumps that use a piston on both sides is called double-acting pumps.
Advantages of Pumps
- Pumps are very useful equipment for transporting liquids.
- From very low to very high capacity.
- It is rotating equipment. It is widely used in many systems such as water-cooling loops, tower cooling loops, etc.
- Low noise compared to other rotating equipment.
- The pump can also use for air supply.
- No losses
- Different structures and materials are used for the pumps.
Disadvantages of Pump
- These machines run smoothly, but cavities can form. This destroys the system.
- It may have corrosion problems.
- In many cases, there may be a problem with fluid intake. For example, reciprocating pumps are not suitable for liquid liquids.
- The centrifugal pumps cannot run without turning on.
- The piston or impeller speed is limited.
Applications of Pumps
- Storage and delivery of water.
- Internal application.
- Applications for sludge and wastewater.
- Fire protection and protection system
- Manufacturing, chemical, oil and gas, pharmaceutical, food, air, conditioning, and other industries.
- Aquarium, fountain, pond filter, and so on
- Pumps are also used in the automotive industry.
- In thermal, nuclear, or hydroelectric power plants, pumps are one of the most important pieces of equipment.