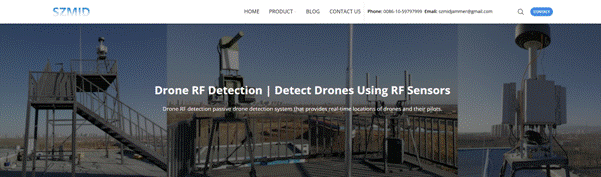
Which Is Better for Security?
The growing competition in technological innovations concerning drone security brings two technologies to compete against each other: drone RF detection and radar-based detection. They are practically components of any counter-drone systems but have specific advantages and difficulties. Apart from these technologies, Audio Jammers are also currently being incorporated with detection systems to enforce effectiveness in jamming drone communications. This article, therefore, shows the difference between the two: RF detection systems and radar technology, hence setting it best for knowing the strengths and weaknesses they possess in the context of drone detection and security.
What is your understanding regarding RF detection?
RF (Radio Frequency) Detection is, rather simply, a method of monitoring radio frequencies utilized in communication between any drones and their operators. Control and navigation of drones are largely RF signal dependent, often operating in specific frequency bands (2.4 GHz, 5.8 GHz, or even more specialized bands). RF detectors receive these signals and analyze them to determine the presence and location of drones.
How RF Detection Works
- Signal interception: The system listens for radio signals emitted by the drone and its controller.
- Signal analysis: It decodes the frequency, power, modulation, and unique characteristics of the drone’s RF signature.
- Drone identification: By analyzing these signals, the system can distinguish between drones and other wireless devices.
What Is Radar Detection?
Radar sets for radio detection and Ranging detect matter in the atmosphere using radio waves as their medium of transmission. The above-mentioned systems emit electromagnetic waves, which are reflected back to the radar receiver after interacting with some object (in this case, a drone). The distance, speed, and position can then be calculated by radar systems by measuring the time taken for the return waves and by analyzing the reflected signals.
How Radar Detection Works:
- Wave transmission: The radar sends out radio wave signals into the open air.
- Wave reflection: When a drone under radar coverage enters the coverage area, waves reflect from the drone.
- Signal processing: Based on the calculated returned signals, the system determines the position, speed, and trajectory of the drone.
Strengths of RF Detection
- Specific Detection:
- Drone RF Detection was developed specifically to identify and track wireless communications signals transmitted from drones. It is thus very efficient in detecting drones even when drones fly at non-visible frequencies or low altitudes, as in urban environments.
- Low Power Consumption:
- RF detection systems tend to consume less power than radar systems. This makes them a better option for continuous, real-time monitoring in security systems that need to be active 24/7.
- Drone Identification:
- RF detection can often identify specific drone models based on the unique characteristics of their RF signals (like the manufacturer, model, and operational mode). This provides detailed intelligence, which is a major advantage in security operations.
- Stealth and Covert Detection:
- RF detection systems are passive, which means that they do not emit any signals. Hence, the drone is completely unaware of being detected, thus proving essential in covert security operations and monitoring against potential threats.
- Interference with drones:
- Many RF detection systems are integrated with jamming technology that can disrupt the communication between the drone and its operator. This can force the drone to land or return to its starting point, providing an effective method of neutralizing the threat.
Strengths of Radar Detection
- It has long-range detection capability.
- A radar system can detect a drone at a distance several times greater than that possible with an RF system. Depending on the power and configuration of the radar, it can detect objects from various kilometers for wide-area surveillance purposes. According to the specific applications of radar technology for drone tracking, drone detection radar is one of the best applications. Drone Detection Radar in particular is designed and developed to improve other radar systems by enhancing their capabilities for sensitive detection and tracking of drones in a very complicated environment.
- All-weather compatibility.
- Radar can work in fog, rain, or even nighttime when the detection of RF signals fails. Since radar does not depend on light sources or atmospheric conditions, it can operate reliably in difficult environments. Detection of Multiple Objects: Radar systems are designed to track multiple objects at the same time. In high-traffic areas, this feature also allows the radar systems to manage sightings of many drones or other flying objects at once; thus, it will become helpful during busy or comparatively sensitive airspace management scenarios.
- Not dependent on the communication signals:
- Without releasing RF signal radiation from the drone, it can detect helicopters and/or drones based on radar operation. Thus, it captures the very important drone, which is utilizing encrypted or sometimes nonstandard communications of nonstandard detection types.
- Long-range detection:
- They can usually detect drones over a much greater distance compared to an RF system. Depending on the power and design of the radar, it can detect, at a distance of almost several kilometers, such an object, which should ideally have wide-area surveillance. Drone Detection Radar applications are among the best when it comes to radar technology for tracking drones. It is specifically constructed and created to improve other radar systems by bettering sensitivity for detecting and tracking drones even in very complicated environments.
Weaknesses of RF Detection
- Limited Range:
- RF detection is generally effective only within a limited range, typically up to a few kilometers. This can make it unsuitable for monitoring large, open areas or for situations where early detection of a drone is crucial.
- Subjective to Signal Interference:
- Disruption in RF detection systems is brought about by the interference of other neighboring electronic devices or sources of RF signals. Examples of such things that could create interference noise include commercial wireless networks, Wi-Fi, or even the presence of other nearby drones. These noises will make the accuracy in the detection of drones more difficult.
- Line-of-Sight Limitations:
- A RF detection system needs a direct line of sight to the communicated signals to be able to properly locate the drone. A drone that flies behind buildings, mountains, or other objects can easily escape detection.
- Limited Detection of Non-Communicating Drones
- An even greater challenge is posed when a drone is flying without issuing detectable RF emissions (and thus detectable by RF detection, like in autonomous mode) because it does not actively communicate with the operator.
Weaknesses of Radar Detection
- Limited Identification Capabilities:
- The basic ability of radar is to detect a given object, whether it exists or moves, but nearly always it cannot provide the specification of what type of drone it is. Obviously, it can get the speed, direction, and altitude of the drone but is not capable of differentiating one type of drone from another or the intention of the operator behind the controls.
- High power consumption:
- Radar systems are higher-energy-consumption systems than the other RF systems for detection; for long-range or larger scanning areas, radar systems are quite expensive to operate; this situation becomes much more severe in continuous monitoring scenarios.
- Vulnerable to drones using stealth technology
- Drones that utilize stealth technologies or specialized materials that are designed to reduce radar signatures (lower radar cross-section, etc.) may evade detection from certain radar systems; therefore, radar applications become ineffective against advanced or military-grade drones.
- Weather sensitivity:
- Though radar is capable of running under many environmental conditions, there are also some sorts of conditions that can possibly interrupt its operation through severe weather. Heavy rainfall, snow, or hail may scatter the radar waves, therefore leading to degradation in the accuracy of detection.
How to choose?
The choice between drone RF detection and radar detection depends on the specific security needs and environment.
- For precision and targeted security, especially in environments with a high concentration of RF activity (e.g., airports or public events), RF detection is ideal. It provides the ability to specifically identify drones and their operators while remaining covert and consuming less power.
- For large-scale, all-weather surveillance, where long-range detection and the ability to track multiple objects simultaneously are required, radar detection is a better option. It is also the preferred technology for scenarios where detecting all flying objects (regardless of whether they are drones) is critical, such as military or large perimeter security.