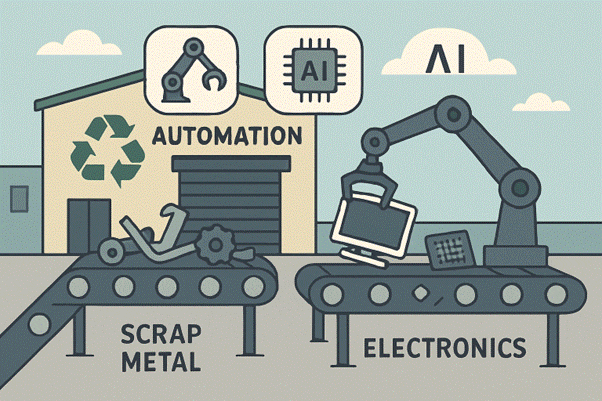
As the demand for raw accoutrements intensifies and environmental mindfulness grows, recovering scrap essence and electronic waste (e-waste) has become a foundation of ultramodern sustainability efforts. Effective recycling practices help conserve limited natural coffers and check pollution, enabling communities and diligence to thrive economically while recognising environmental stewardship. Companies and individualities likewise can contribute to this movement through comprehensive metal recycling services for residential and commercial use, ensuring that precious coffers are recovered and dangerous waste is duly managed.
The significance of advanced recycling styles has nowhere been further apparent. By embracing transformative technologies and sustainable practices, we help pollution, limit tip
impact, and support the indirect frugality. Discarded electronics and scrap essence aren’t mere trash; within them are critical minerals and essence vital for unborn technology and profitable growth. These results reveal an interdependent relationship between environmental preservation and resource recovery, setting the root for sustainable development.
Advancements in Recycling Technologies
Recent improvements have streamlined the processing and recycling of scrap essence. Installations now use state-of-the-art shredders with high-powered motors that break down large assemblies into recoverable factors. Robotisation is a crucial motorist — detector-sorting and glamorous separation enable rapid-fire sorting and the birth of pure essence from mixed debris. These inventions not only ameliorate material recovery rates but also minimise the reliance on homemade labour. As a result, recovery centres can reuse advanced volumes of scrap, reduce reversal times, and achieve emotional functional effectiveness in situations.
Automated processing also contributes to more precise material brackets, resulting in better product quality and a significant drop in impurity rates. By reducing the chance of recoverable essence that end up in tips
These advancements help foster both environmental and profitable substance.
Artificial Intelligence in Recycling
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine literacy (ML) are reconsidering the boundaries of material recovery. AI-powered systems dissect the composition of incoming material aqueducts in real time, enabling the dynamic adaptation of sorting parameters. For illustration, AI can distinguish aluminium from a sword or sort bobby cables from other debris with inconceivable delicacy. This position of optimisation reduces waste and boosts overall recovery rates.
Machine literacy algorithms continually upgrade these processes, conforming to new material combinations and types of impurity. As a result, installations using AI stand at the van of the recycling revolution, creating cleaner product aqueducts and reducing the burden on both mortal workers and tips
Environmental Impact E-Waste
E-waste disposal remains a pressing global issue, with millions of tonnes exported annually, frequently under pretence and without acceptable environmental safeguards. Similar practices inflict annihilation on fragile ecosystems, poisoning soil and water and exposing vulnerable workers to poisonous rudiments like lead, mercury, and honey retardants. According to a report by the Basel Action Network, lax oversight in transnational e-waste trade has accelerated pollution in several developing regions, pressing the critical need for responsible recycling pathways.
Innovative E-Waste Recycling styles
Safer, further sustainable recovery of critical accoutrements from electronic waste is making captions. For illustration, Australian experimenters have innovated a system that replaces poisonous chemicals with trichloroisocyanuric acid—a detergent formerly used in water treatment—to insulate gold from discarded circuit boards. This invention achieves nearly perfect chastity and significantly reduces the health pitfalls associated with traditional gold birth styles.
In addition to chemical innovations, advanced ferrous and non ferrous metal recovery equipment is increasingly being deployed to efficiently separate and reclaim valuable metals from complex e-waste streams.
Other approaches now being gauged up include the use of bioleaching microorganisms to recover precious essence and unrestricted-circle hydrometallurgical systems designed to capture and exercise as much important material as possible. These ways are essential for reducing chemical runoff and ensuring that as much important material as possible is reintegrated into new manufacturing cycles.
Government enterprise and Support
Feting the need for invention in the recycling ecosystem, governments in the U.S. and around the world are ramping up their support through backing and policy impulses. The U.S. Department of Energy, for illustration, established the Electronics Scrap Recycling Advancement Prize (E-SCRAP) programme, which provides financial awards for promising e-waste recycling systems. Similar enterprises aim to goad the exploration and commercialisation of critical material recovery styles, thereby reducing reliance on imported minerals and supporting domestic manufacturers.
Economic openings in Recycling
Recycling also energises job creation and original profitable revivification. Case in point:
Aurubis AG, the primary Bobby patron in Europe, lately opened a state-of-the-art recycling factory in Georgia, USA. This installation is capable of processing over 180,000 metric tonnes of scrap material annually, efficiently and complexly, into high-grade bobby and other precious derivations. Similar systems not only cut down import dependence but also boost indigenous employment and contribute to the development of new, cleaner diligence.
Conclusion
Embracing sustainability results in scrap essence recycling, which is pivotal for striking a balance between profitable growth and environmental protection. Advanced sorting technologies, AI-driven innovative birth processes, and strong government and private sector support are inclusively steering in a new period of responsible material recovery. These efforts give a design for communities, diligence, and policymakers worldwide to alleviate the pitfalls associated with dangerous waste, conserve our remaining coffers, and harness the profitable benefits essential in recycling. By taking decisive action in the moment, we can make a more sustainable, indirect frugality for generations to come.