Ultramodern dental implant procedures have been revolutionised by technological advancements, delivering greater perfection, effectiveness, and comfort than ever before. From enhanced planning tools to minimally invasive surgeries, technology plays a pivotal part in addressing successful issues for cases seeking dental restoration. Understanding how these inventions impact care is essential for those considering implants or seeking the most advanced dental treatment options. For cases assessing treatment choices, understanding the the full mouth dental implant cost Dallas, TX, can also help in planning and decision-
Dental technology not only shortens recovery times but also increases the safety and pungency of procedures. Cases can now anticipate acclimatised results that enhance the fit and function of dental implants, all while minimising discomfort. As the dental assiduity adopts digital dentistry, new possibilities for case-centric care crop up daily.
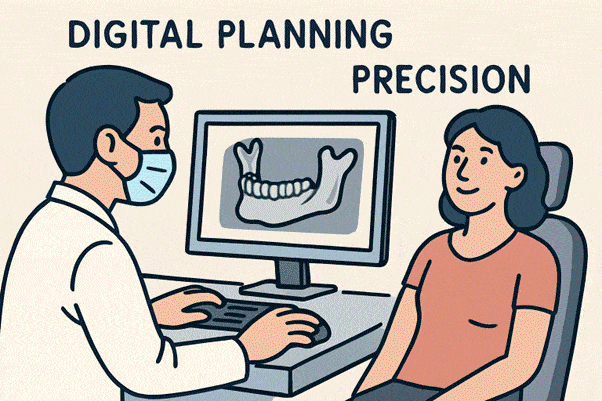
Digital Imaging and Planning
One of the first steps in dental implantology is opinion and treatment planning, where digital imaging tools similar to Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) have become necessary. CBCT reviews give three-dimensional views of a case’s jawbone, jitters, and girding apkins. This position of detail significantly enhances the delicacy of assessments, enabling the tailoring of implant placement to each case’s unique requirements. With digital planning, dentists can precisely determine the exact confines and exposure of every implant, significantly reducing the threat of complications.
In addition to delicacy, digital imaging allows for further transparent communication between clinicians and cases. Dentists can show cases their reviews and explain the recommended course of treatment, giving them less confidence throughout the process. According to the American Dental Association, ultramodern imaging modalities enhance diagnostics for implant campaigners, thereby helping to ensure long-term implant health.
Computer-Guided Surgery
Technological progress doesn’t stop at planning. Computer-guided surgery leverages the digital information gathered during planning to produce surgical attendants. These attendants are custom-fabricated templates that fit directly over the case’s teeth and epoxies, guiding the dental surgeon’s hand to ensure precise positioning, angulation, and depth for each implant. As a result, implant procedures are less invasive and, importantly, faster than traditional ways. This frequently allows for quicker mending and lower postoperative discomfort for cases.
By minimising room for error, computer-guided surgery has set a new standard in safety and effectiveness. Studies stressed by Healthline show that delicacy and case satisfaction are greatly increased, especially in complex cases where precise placement is critical to success.
Intraoral Scanners
Intraoral scanners have excluded the need for messy print accoutrements preliminarily needed for dental moulds. These handheld devices digitally capture the bias of the geomorphology of a case’s teeth and epoxies within twinkles, furnishing moment-high-resolution 3D images. Dental labs use these digital prints to design and fabricate custom crowns, islands, and abutments that fit seamlessly with implants.
Case Comfort and Speed
For cases, the experience is more comfortable and less protrusive than traditional styles. For providers, digital prints enable better communication with labs and significantly reduce the time needed to deliver final restorations.
Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry
AI tools are fleetly changing the geography of dental implantology. Software equipped with machine literacy algorithms can dissect radiographic images to identify optimal implant locales, descry abnormalities, and flag eventual complications. AI can indeed help in creating individualised surgical plans that balance function, aesthetics, and life.
Prophetic Analytics in Implantology
With the aid of AI, the prophetic power for determining whether a procedure will succeed has increased. This translates into reduced pitfalls for cases and lesser effectiveness for dentists. AI also streamlines attestation and charting, freeing up clinicians to spend further time with their cases.
Robotic backing in Implantology
Robotic systems are beginning to make their mark in dental surgeries. Robots can help surgeons by situating tools, guiding drills, and icing implants that are placed with millimetre delicacy. The use of robotics minimises mortal fatigue and variability, two major factors that impact surgical perfection. Specifically, in 2017, a robot performed a completely independent dental implantation in China, showcasing the safety and trustworthiness of robotics in clinical care.
3D Printing in Dental Implants
3D printing, also known as cumulative manufacturing, is revolutionising the production of dental implants and their associated accessories. With this technology, case-specific surgical attendants, implant abutments, and indeed custom titanium implants can be fabricated snappily and affordably. Dentists can ensure the factors fit each patient impeccably, perfecting issues and comfort.
3D printing also expedites the delivery timeline, reducing the delay for cases seeking endless tooth restoration. This approach is poised to homogenise access to dental implants further as costs drop and customisation becomes more commonplace.
Smart Dental Implants
The development of smart implants equipped with biosensors is one of the most instigative borders in drugs. These detectors can descry changes in temperature, pH, and indeed pressure around the implant, giving early warning of infection or prosthetic failure. Dentists can act instantly to help complications before they escalate.
Monitoring Health and Supporting Life
Real-time feedback from smart implants may soon become the standard of care, enabling not only safer implant surgeries but also more effective ongoing conservation for times to come.
Final studies
The relinquishment of technological inventions is transubstantiating every aspect of the dental implant process, from planning and surgical placement to long-term conservation and care. Digital imaging, computer guidance, AI-supported analytics, robotics, and 3D printing are making dental implants safer, brisker, and more dependable for cases far and wide. Individualities seeking to restore their grins can now anticipate the loftiest position of perfection and care, performing in better issues and a brighter future in dental health.